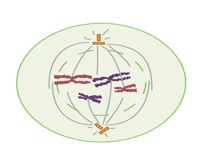
This cell is in which stage of mitosis?
A. Early Prophase
B. Telophase
C. Metaphase
D. Anaphase.
E. Gap1 phase arrest
F. Gap2 phase
Please circle the letters that precede the most appropriate answer(s) to the question asked. Circling more than one letter in answering any given question will count against you.
1. Evolution of species on Earth
A. has stopped.
B. occurred only in the distant past.
C. only occurred after the Cambrian explosion.
D. has occurred throughout Life’s history and is still under way.
E. None of the above
2. The modern polar bear species has potentially evolved from ancestral species of bears that populated southern Alaska, but which became separated by glaciers from bear populations in the rest of North America. The general term for this type of event would be called a(n):
A. allopatric speciation.
B. temporal isolation.
C. mechanical isolation.
D. sympatric speciation.
E. glacial speciation
F. parasympathetic specialization
3. Consider the figure below. This cell is in which stage of mitosis?

This cell is in which stage of mitosis?
A. Early Prophase
B. Telophase
C. Metaphase
D. Anaphase.
E. Gap1 phase arrest
F. Gap2 phase
4. The biological species concept (BSC) states that:
A. species are groups of potentially interbreeding natural populations which are reproductively available to all other such groups.
B. species are groups of actually interbreeding populations which are sometimes reproductively isolated from other such groups.
C. species are groups of actually, or potentially interbreeding natural populations which are reproductively isolated from other such groups.
D. species are groups of actively interbreeding natural populations, which are reproductively similar to other such groups.
E. species are groups of potentially interbreeding subpopulations, which are reproductively isolated from other such groups.
5. The purpose of Mitosis Is to:
A. Help an Organism grow larger.
B. Produce the Sex gametes.
C. duplicate the cell while maintaining genetic constancy.
D. provide for genetic mutations.
E. Provide for Genetic variation through Genetic Drift.
6. A “hinny” is an example of:
A. A hybrid offspring that is an example of a prezygotic barrier.
B. A consequence of spatial isolation resulting in gametic interactions
C. A hybrid offspring that is an example of a postzygotic barrier.
D. A consequence of postsynaptic rigor.
E. A wonderful and friendly four legged rodent.
F. A hybrid offspring that is an example of a postsynaptic barrier.
G. A consequence of hybrid vigor.
7. According to information specifically given in one of the lectures a classical example of “adaptive radiation” can be seen in
A. Peppered Moths.
B. Mules
C. Darwin’s finches.
D. Hawaiian finches .
E. Ecuadorian blackbirds
8. In the hypothetical phylogenetic tree shown below, which groups, inclusive of any ancestors, are monophyletic?
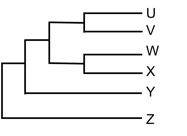
A. Y & Z
B. U & V, W & X
C. U & V & W
D. W & X & Y & Z
E. None of the above
9. In which phase of a cell’s cycle is the majority of its DNA replicated ?
A. Prophase
B. Interphase
C. Anaphase
D. Prometaphase
E. Gap1 phase
F. Interkinesis
10. What is the generic “currency” of energy for most living organisms?
A. Oxygen
B. Water
C. ATP
D. Vitamin B12
E. OTU
F. AMP
11. What kind of selection is occurring if both the smallest and the largest individuals contribute relatively more offspring to the next generation than those closer to the average height?
A. Disruptive selection
B. Stabilizing selection
C. Disruptive selection and stabilizing selection
D. Directional selection
E. Directional selection and stabilizing selection
12. According to one of the movies… “Evolution -when taken to its logical conclusion”- would suggest that:
A. All living organisms share a common heritage.
B. Shared traits always suggest a shared heritage.
C. Mass extinction of species is a necessary consequence of evolutionary change.
D. All of the above.
E. A and B only.
13. The term “carrying capacity” refers to:
A. The ability of animals -such as pandas- to hold or carry bamboo shoots.
A. The limits of a population that are defined by its genetic variation.
B. The number of genes within a given population.
C. The maximal population size within a given environment.
D. The number of obvious phenotypic traits that arise in a population.
14. According to the arguments detailed in the class, thus far, which of the following is NOT a cause for change or variation in the genetic structure of a given population?
A. Mutation
B. Gene flow
C. Genetic drift
D. Cell division
E. Natural selection
15. Which one of the following statements distinguishes a prokaryotic cell from a eukaryotic cell?
A. The prokaryotic cell has a nucleus.
B. The eukaryotic cell is often much smaller.
C. The eukaryotic cell has a nuclear membrane.
D. The prokaryotic cell has at least one cell membrane.
E. The prokaryotic cell is a single celled organism.
If all statements above are true then circle “F”.
If all statements above are not true then circle “G”
16. Why do you think that the first organisms on the earth might have been anaerobic?
A. Because you don’t need a nucleus to grow anaerobically,
B. The first eukaryotic cells only emerged around 2.7 billion years ago (bya),
C. Because there was little oxygen around at that time, ~4.2 bya.
D. Even though 600 mya, oxygen levels in the atmosphere were considerable, evolution of aerobic cells is more complex.
E. Difficult to say, perhaps because mitochondria had not evolved yet.
17. According to the arguments detailed in the class, thus far, which of the following is NOT a cause of change in the genetic structure of a given population?
A. Mutation
B. Gene flow
C. Genetic drift
D. Cell division
E. Natural selection
18. The average bacterial cell is approximately:
A. 1.5 – 3 µm in length,
B. 1 - 5 nm in length.
C. 100-500 µm in length.
D. 1m in diameter.
E. 1mm in diameter.
20. How small / large is Thiomargarita magnifica?
F. 1.5 – 3 µm in length,
G. 1 - 5 nm in length.
H. 106 µm in length.
I. 1m in diameter.
J. 10 mm in diameter.
Bonus Points (2pt): Other than Thiomagarita magnifica, correctly name one bacterium
__Escherichia_____ ____coli_______,
What is it’s Genus? ___ Escherichia ___
Section 1b (19 pts.)
In the next few answers, label the figures and from the list of words given please insert the most appropriate word(s) into the spaces provided and then answer any other additional questions.
20. (a) (4 pts) Place the categories listed below in their correct order of hierarchy –according to Linnaean grouping (you can go up or down –it doesn’t matter).
Domain, Genus, Kingdom, Class, Phylum, Species ,
______D________ ______K_________ ______P_________ _______C_________
_______G_______ _______S_______
(a) (2 pts) Which category(ies) is (are) missing?
________Order________ _____Family_______
21 (a) (3 pts) Given the available possibilities, please correctly label (write in) the various structures / cell cycle phases in the figure below (1pt each correct label).
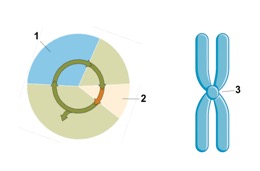 1. S – phase, 2. Cell division
/Mitosis (thus far in the course), 3. Centromere
1. S – phase, 2. Cell division
/Mitosis (thus far in the course), 3. Centromere
A. Telophase
B. Metaphase
C. Mitosis
D. Gap 1 phase
E. Meta-Prophase
F Ataphase
g. Anaphase
(b) (2 pts) Given your knowledge of Cell division, indicate in the list above which of the phases of Mitosis would the represented chromosome (above) be found.
22. Allele Frequencies, Aponymous Frequencies, Phenotype, Equanimity,
Gene flow, Mutualism, Genetic Drift, Gene Pool, Random Drift, Onomatoplasia, Non-Darwinian Selection, Genetic toolkit, Genetic Frequencies, Commensalism.
(a). (2 pts) The frequencies of the variant types of genes being present in a population are called _ Allele Frequencies _
(b). (2 pts) The _ Gene Pool __ is the sum total of genetic information in a population at any given moment. It includes every allele at every locus in every organism within that population.
(c). (2 pts) In a small population, small changes in the allele frequencies over time result from chance events and this is called
__ Genetic Drift ___.
20. (2 pts) Food, Shelter, Genotype, Disease, Predation, Genetic Drift
Choosing from the preceding list, “Environmental limitations on a Population’s growth” include:
___ Food _____, ___ Shelter ____, ____ Disease ______, ___ Predation ___ “
Please answer the following questions either using short, concise answers, or by explaining why you made appropriate changes that you have to any figure -again using short, concise explanations.
2.1 (6 pts.) Compare and contrast the terms “Allopatric” and “Sympatric” speciation events. Give an example of one.
Allopatric speciation occurs in separate, non-overlapping geographical areas, that is normally
separated by a significant geographic barrierl
Sympatric speciation occurs in in populations while bot continue to inhabit the same geographic location,
i.e no geographic barrier
lecture 5 halfway down
________________________________________________________________________________
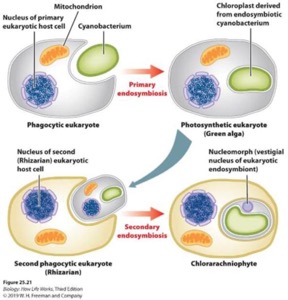
2.2 (6 pts.) Given your knowledge of evolutionary development of organisms discuss one of the hypotheses as to the origins of heterotrophic and photosynthetic eukaryotic cells from more simple cellular forms.
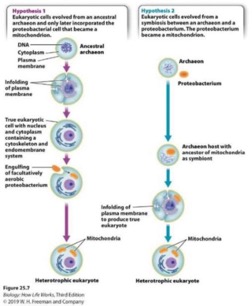 _
_
_______________________________________________________________________________
2.3. (6 pts.) Briefly discuss some of the differences between “Gram positive” and “Gram negative” bacteria.
Fundamentally, Gram positive cells have a singular cell membrane surrounded by a very thick murein layer,
while Gram negative cells have two membranes, creating the “periplasmic space” (effectively an organelle)
in which there is a thin layer of “murein sheath (peptidoglycan layer), which provides rigidity and strength to
the cell.
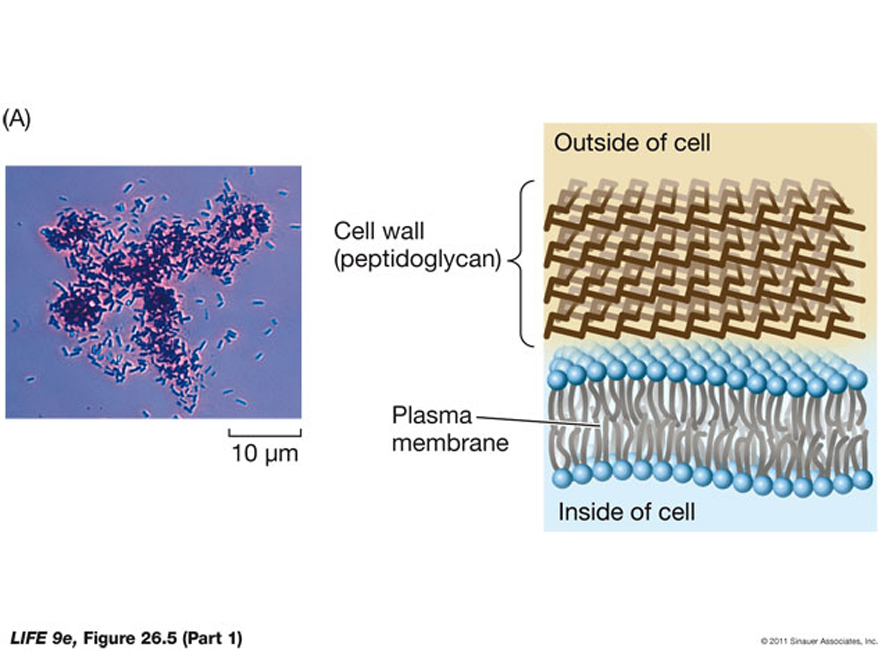
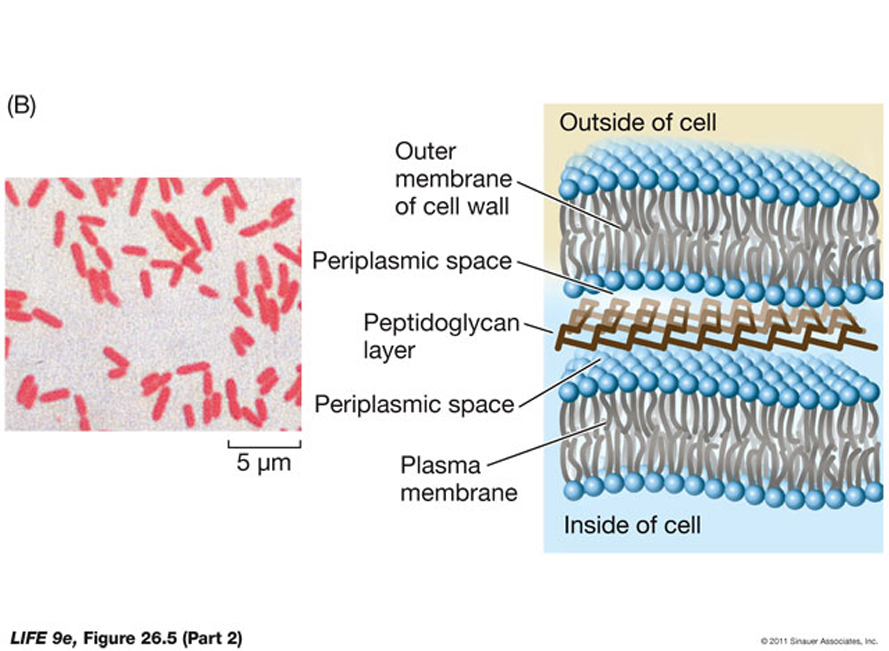
________________________________________________________________________________
2.4a. (6 pts.) List three quite distinct differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Murein sheath/layer, size, method of cell division, presence/absence of nucleus, presence/absence of
multiple organelles etc,
2.4b. (4 pts.) Give TWO similarities between archaea and eukaryotes, which would indicate evolutionary relationships between the two.
Cell membrane, cellular organization, organelle(s), potential histones, introns, RNA polymerases etc. L & D isomers of amino acids and carbohydrates, central dogma etc. effectively any similarity that suggests a “common heritage”.