Biology 2107 Fall, 2023
Test #2
Name: __________________________ Student ID: __________________
Please circle the letters that precede the most appropriate
answer to the question asked. Be aware,
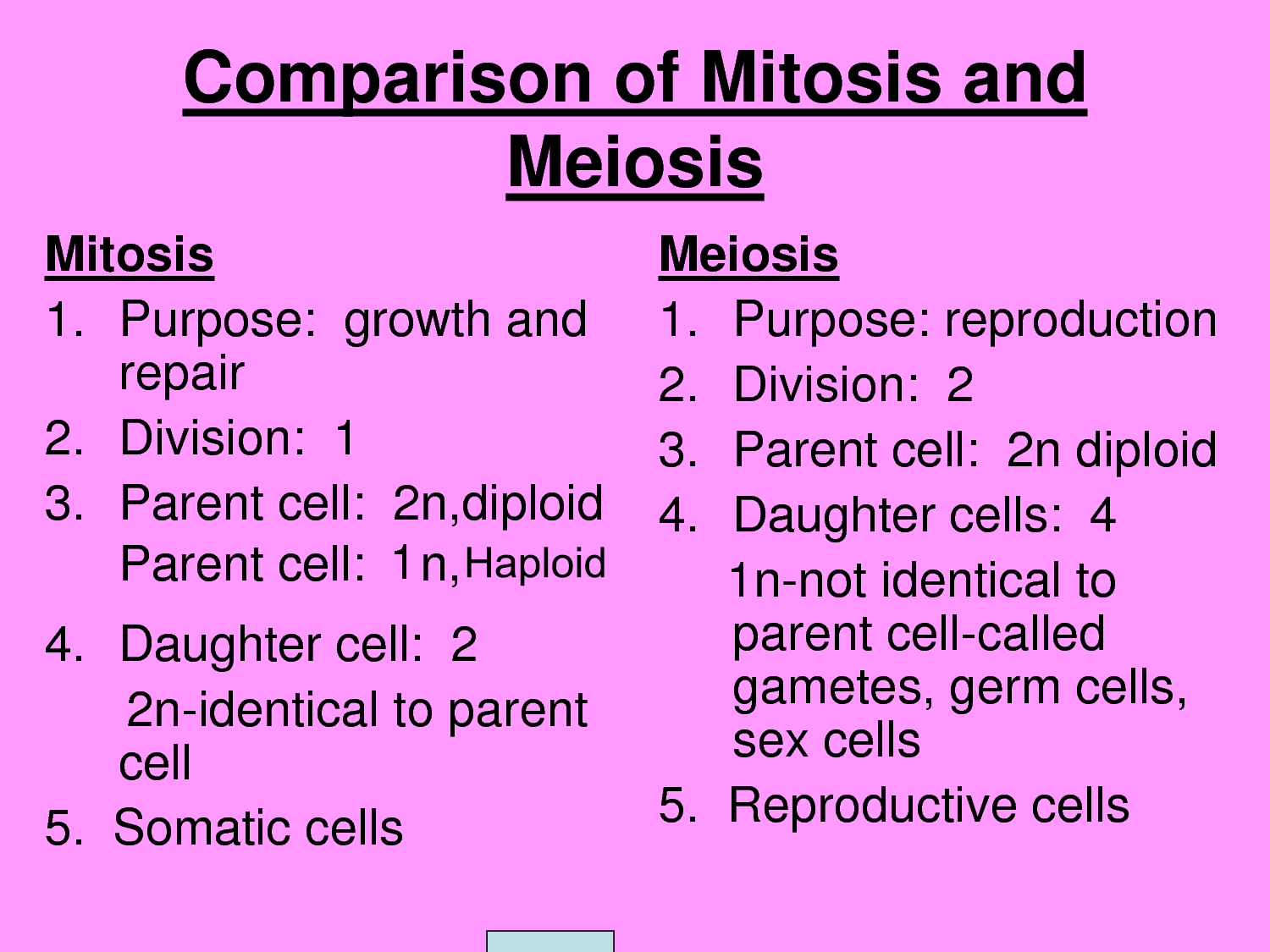
there is only one answer to each question.
Section 1 (20 pts.)
1. Given that, in barley plants, the allele for tall stalks is
dominant over short stalks and the allele for wide
leaves is dominant over thin leaves. Assuming
"independent assortment", what would be the best way to determine the
genotypes of a given barley plant that exhibits tall stalks and wide leaves?
A Undertake a "Test cross" between a Tall stalk and
thin leafed barley plant against itself
B Undertake a "Test
cross" between a Tall stalk and Wide leafed barley plant with a short
stalk and wide leafed barley plant
C Self cross a Tall stalk and Wide leafed barley plant
D Undertake a "Test cross" between a Tall
stalk and Wide leafed barley plant against a short stalk and thin leafed
barley plant
E Review BIOL2107 notes, just one more time… not a viable
option, at this time.
2. How many “valence” electrons does carbon have
in its outer shell?
A.
2
B.
3
C.
5
D.
4
E.
7
3. In Labrador retrievers, the allele for a
black coloured coat (B) is dominant to the allele for
brown fur coat colour (b). However, if a lab has two
copies of the "recessive allele" for a "pigment-depositing
gene" (e), it can only have yellow coloured fur.
In a cross of two doubly heterozygous black labs (BbEe
x BbEe), what fraction of the next generation would
one expect to have yellow fur?
A.
3/8
B.
1/8
C.
1/16
D.
1/4
E.
5/8
4. Given its ability to scrutinize allelic
frequencies, the Hardy Weinberg equilibrium can determine..
A.
Precisely
when a population will become extinct
B.
Precisely
when a population became extinct
C.
The geographic
movement of a population over time
D.
When a population went
through a disaster, such as a “bottleneck”
E.
How
long life has been around on earth
5. At which phase in cell division do homologous
chromosomes segregate
A.
Anaphase II of Meiosis
B.
Prophase I of Meiosis
C.
Metaphase II of Meiosis
D.
G phase 2 of Mitosis
E.
Anaphase I of Meiosis
F.
Metaphase of Mitosis
6. If the atomic weight of sodium is 23, and the
atomic weight of chlorine 35.5. When
58.5 grams of sodium chloride are dissolved in a final volume of 2 liters of
water, the solution is said to be:
A.
0.5 molar
B.
58.5 molar
C.
1 molar
D.
Cannot tell, because you cannot tell
whether sodium chloride is formed between ionic or covalent bonds
E.
23 micromolar
F.
12.5 molar
7. Which one of the following
statements is a good “generalization” -according to the lectures and lecture notes.
A. Bases accept H+;
Acids donate H+
B. If a compound
increases the OH+ ion concentration when added to water, then the compound is
said to be acidic
C. All acids dissolve fully in water
D. Acids
accept H+; bases donate H+
E. The pH value is
defined as the positive logarithm of hydrogen concentration in moles per liter (molar concentration).
8. Hypertrichosis, hairiness of the pinna of the ear, is inherited as a Y-linked trait in humans. If a man with hypertrichosis and a woman (who doesn’t) plan to have children, as both of them had taken BIOL2107, what is the most likely outcome that they can foresee?
A.
All
offspring will have hypertrichosis
B.
Half the offspring will have hypertrichosis
C.
All
the male offspring would be sterile
D.
Only
half the female offspring would express hypertrichosis
E.
All
offspring will have phenotypically normal ears
9. RNA molecules are transported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm
in eukaryotes through:
A
The rough
endoplasmic reticulum.
B The
smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
C The Golgi apparatus.
D Nuclear
pores
E
Liposomes
10. If two genes demonstrate
"independent assortment", which assumption is most likely true?
G. Crossing over between the genes
does not occur
H. The two genes are located on
different chromosomes or are far enough away from each other on
the
same chromosome as to always allow for crossovers to occur.
I.
The two genes are located in very close proximity to each other on the
same chromosome
J.
The two genes are located on the X chromosome
K.
Mendel had something to do with it, and neither is dominant over
the other.
L.
The expression of one gene has NO effect on the expression of the
other
Section 1 B (12 pts).
In the next several questions each question is worth 3 pts.
Please circle your evaluation of the
statement given. If you
believe the statement to be “False” then explain why you think so in the space provided.
Read each question carefully !
11.
With respect to proteins the term “Tertiary
structure” refers to the 3D organization of various protein subunits in
a complex protein,
resulting in the assembled structure of a series of subunits in to a protein,
like haemoglobin.
True False
___this description is for quaternary structure_______________________
12. During Mitosis microtubular
spindle fibres attach to the chromosomes through
“kinetochores”.
True False
____________________________________________________________________
13. Excluding lipids, macromolecules
can be considered to be molecules, whose molecular weight is greater than 999
Daltons.
True False
14. The
“Golgi apparatus” is an organelle in eukaryotes that modifies newly synthesized
proteins for “export” and/or passage
around the cell
True False
Section 2 (53 pts)
Please answer the following questions in the space provided,
using short, concise answers.
2.1
(6 pts.)
(a) Give an example of a disaccharide and state from
what monosaccharide(s) is it formed and how?
____Sucrose from glucose &
fructose, removal of water
(condensation)________________________________
or
____Lactose from glucose & galactose,
removal of water (condensation)_______________________________
or
____Maltose from glucose, removal of
water (condensation)_________________________________________
2.1
(6 pts.)
(b) Define
2 major differences between each the
following types of molecules:
Carbohydrates and Proteins
alpha carbon, amino “acid”s peptide
bonds, vs. CHO, fatty acyl side chains, forming or not form
lipid bilayers, or micelles,
true vs false macromolecules, hormones? Waxy or oily
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Similarities: Fundamentally
Carbon, hydrogen and Oxygen , energy storage/source, CH2O___
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
2.2. (5 pts.) Briefly discuss the
concept of phenotypic changes due to “gene interactions”,
giving at least one specific
example of such an occurrence.
_____Epistasis,
complementary genes, ABO blood groups etc._____________________________________
_____Labradors. Albino’s
Purple Petal colour in pea plants.________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
2.3
(8 pts.)
Differentiate between an ionic bond and
a hydrogen bond: giving an example
of each.
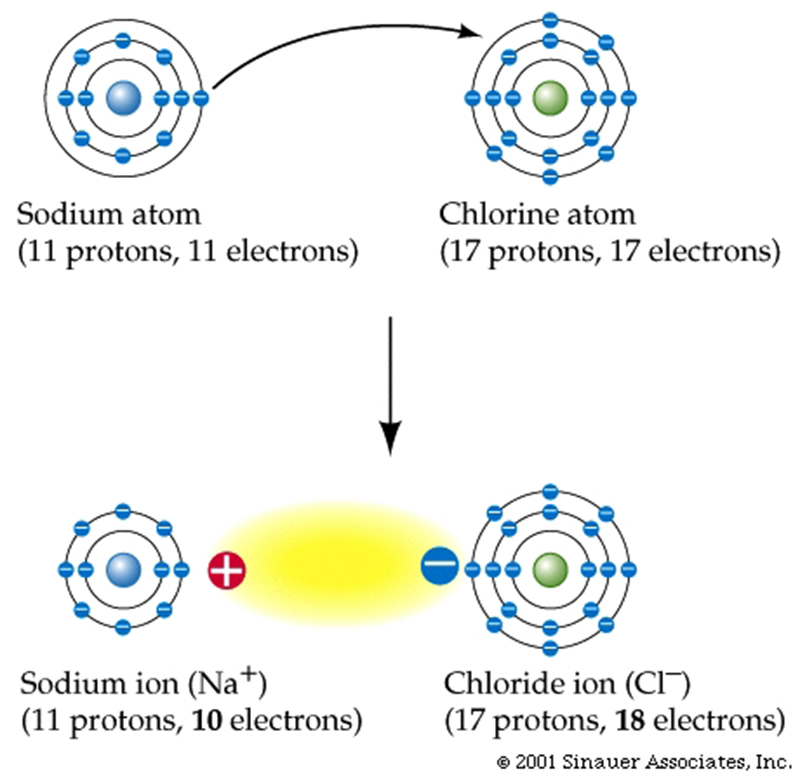
As
opposed to sharing of
electrons_____________________________________________________
2.4.a
(4 pts.) Complete the structures of the two molecules below.
H
H
NH2 – C – COO -
NH2
– C – COO-
I
I
2.4.b
(2 pts.) Explain what makes each of your drawn structures important.
2.5.
(6 pts.) Differentiate between “X”-linkage and “autosomal” linkage.
X-linked inheritance is a pattern of
inheritance in which the transmission of traits depends on the genes in the sex
chromosomes. Only one ZX in males, therefore NO recombination and whatever is
on the X chromosome will be expressed.
Autosomal linkage is when proximal gene pairs on the same chromosome don’t undergo recombination (through chiasmata) with each other to the same extent as they normally would do, and the parental associations are “more frequent”.
2.6
(6 pts.) What is the difference between “Exergonic” and “Endergonic”
reactions
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Exergonic : means "releasing energy in the form of
work". In thermodynamics, work is defined as the energy
moving from the system (the internal region) to the surroundings (the external region) during a given process.
Negative Gibbs free energy.
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Endergonic: chemical
reaction in which the standard change in free energy is
positive, and an additional driving
force is needed to perform this reaction. In
layman's terms, the total amount of useful energy is negative
(it takes more energy to start the reaction than
what is received out of it) so the total energy is a negative net result.
____________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
2.7. (5
pts.)
What’s the difference between “wild-type
trait” and a “dominant trait”? Please
give an
example of a dominant trait that is NOT the
“wild-type” trait.
____Wild type allele is the allele that is present
most in a population, and can be either dominant or recessive (or neither).
Dominant allele is the allele that will normally
show through, even in the presence of its “recessive” allele
_eg. Huntington’s disease._____________ ____________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
2.8. (5
pts.)
The frequency of two alleles in a gene pool
is 0.20 (A) and 0.80(a).
If you assume that the population is in Hardy-Weinberg
equilibrium
Calculate the percentage of individuals with homozygous
recessives for this particular gene in this population.
______p2 +2pq+ p2 =1
_____________________________________________________________________
______0.8 x 0.8 = 0.64 = 64%___________Do not need to calculate the
value all the way______________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
BONUS