
Content coming soon.
.
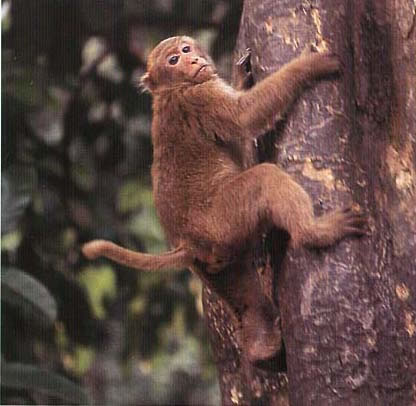

Physical Characteristics:
Head and body length
- male: 431-587mm (17.0-23.1in)
- female: 538-730mm (21.2-28.7in)
Weight
- male: 4.9-8.6kg (10.8-19.0lb)
- female: 7.9-15.0kg (17.4-33.1lb)
Habitat:
Nepal to Viet Nam to Southern China
Monsoon, montane, evergreen, bamboo, and duciduous dry forest at 300-3500m(984-11,484ft) elevation
Diet
Fruit, young leaves, insects, crops, and mammal prey
Behaviour:
Diurnal, arboreal, and terrestrtial. These macaques have been observed frequenting the high canopy

Physical Characteristics:
Head and body length
- male: 431-587mm (17.0-23.1in)
- female: 538-730mm (21.2-28.7in)
Weight
- male: 4.9-8.6kg (10.8-19.0lb)
- female: 7.9-15.0kg (17.4-33.1lb)
Habitat:
Nepal to Viet Nam to Southern China
Monsoon, montane, evergreen, bamboo, and duciduous dry forest at 300-3500m(984-11,484ft) elevation
Diet
Fruit, young leaves, insects, crops, and mammal prey
Behaviour:
Diurnal, arboreal, and terrestrtial. These macaques have been observed frequenting the high canopy
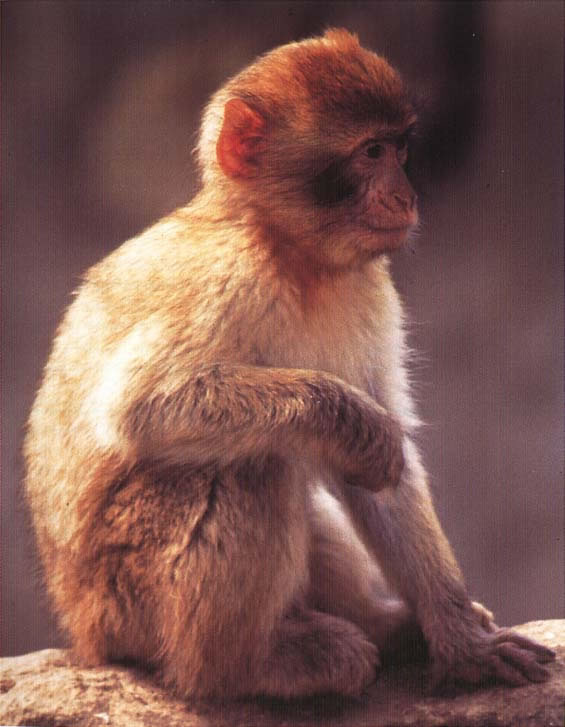

Physical Characteristics:
Head and body length
- Male: 450mm (17.7in)
- Female: 550-600mm (21.7-23.6in)
Weight
- Male: 10.2-11.0kg (22.5-24.2lb)
- Female: 15.3-17.0kg (33.7-37.5lb)
Habitat:
Morroco, Algeria, Gibraltar
Mixed cedar and holm oak or cork ork forest up to 1600-2160m (5260-7087ft)
Diet
Acorns; bark, cones, and needles of cedar trees; mushrooms; bulbs; animal prey, including insects, other invertebrates, and amphibians. The diet changes seasonally.
Behaviour:
Diurnal, arboreal, and terrestrtial. These macaques forage in trees, on the ground, and even under rocks. Males associate with infants soon after birth. There is little male aggression
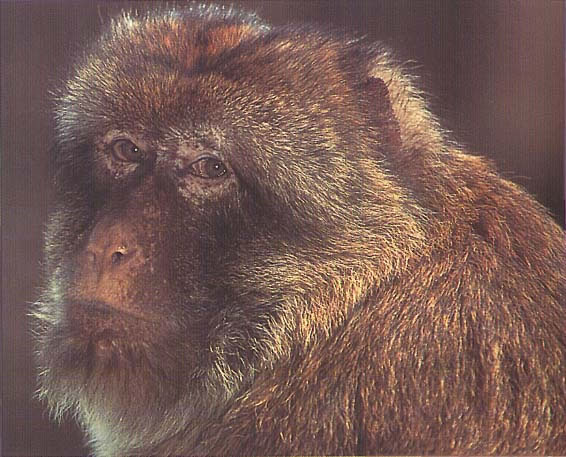

Physical Characteristics:
Head and body length
- Male: 450mm (17.7in)
- Female: 550-600mm (21.7-23.6in)
Weight
- Male: 10.2-11.0kg (22.5-24.2lb)
- Female: 15.3-17.0kg (33.7-37.5lb)
Habitat:
Morroco, Algeria, Gibraltar
Mixed cedar and holm oak or cork ork forest up to 1600-2160m (5260-7087ft)
Diet
Acorns; bark, cones, and needles of cedar trees; mushrooms; bulbs; animal prey, including insects, other invertebrates, and amphibians. The diet changes seasonally.
Behaviour:
Diurnal, arboreal, and terrestrtial. These macaques forage in trees, on the ground, and even under rocks. Males associate with infants soon after birth. There is little male aggression
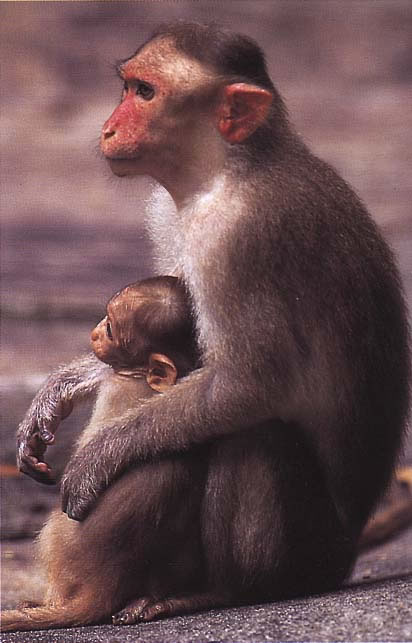

Physical Characteristics:
Head and body length
- Male: 375-480mm (14.8-18.9in)
- Female: 450-590mm (17.7-23.2in)
Weight
- Male: 3.9-4.4kg (8.6-9.8lb)
- Female: 5.4-8.8kg (11.9-19.5lb)
Habitat:
India
Wet lowland to dry deciduous forest up to 2134m (7002ft). Bonnet macaques also live near urban areas and temples.
Diet
Fruit, 47-53$; seeds, leaves, flowers, and animal prey, including insects, lizards, and frogs. Bonnet macaques eat 39 plant species, as well as raid crops and eat what humans offer at temples.
Behaviour:
Diurnal, arboreal, and terrestrtial. Bonnet macaques are good swimmers. They search the ground for insects and chase flying grasshoppers; adult males spend more time on the ground. These macaques sit in contact with others or huddle together when they rest.
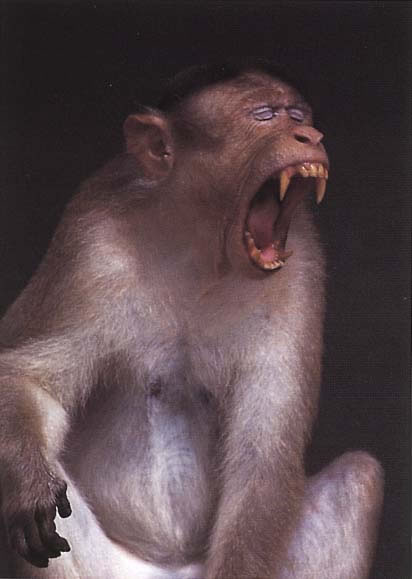

Physical Characteristics:
Head and body length
- Male: 375-480mm (14.8-18.9in)
- Female: 450-590mm (17.7-23.2in)
Weight
- Male: 3.9-4.4kg (8.6-9.8lb)
- Female: 5.4-8.8kg (11.9-19.5lb)
Habitat:
India
Wet lowland to dry deciduous forest up to 2134m (7002ft). Bonnet macaques also live near urban areas and temples.
Diet
Fruit, 47-53$; seeds, leaves, flowers, and animal prey, including insects, lizards, and frogs. Bonnet macaques eat 39 plant species, as well as raid crops and eat what humans offer at temples.
Behaviour:
Diurnal, arboreal, and terrestrtial. Bonnet macaques are good swimmers. They search the ground for insects and chase flying grasshoppers; adult males spend more time on the ground. These macaques sit in contact with others or huddle together when they rest.

Physical Characteristics:
Head and body length
- Male: 500mm (19.7in)
- Female: 590mm (23.2in)
Habitat:
Sulawesi (Indonesia)
Tropical forest.
Diet
Fruit. Booted macaques raid cacao crops.
Behaviour:
Diurnal and arboreal. Poisoned bait is used to kill booted macaques that raid cacao plantations.
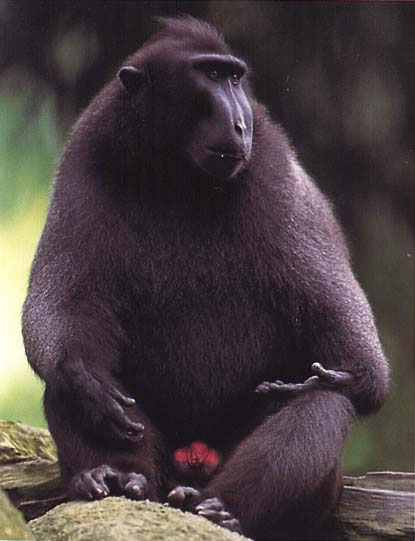

Physical Characteristics:
Head and body length
- Male: 445-550mm (17.5-21.7in)
- Female: 520-570mm (20.5-22.4in)
Habitat:
Sulawesi (Indonesia)
Primary and secondary tropical forest.
Diet
Fruit, bud, sprouts, and insects, including caterpillars. These macaques use 120 plant species.
Behaviour:
Diurnal, arboreal, and terrestrtial. Black macaques show less agonistic behavior (3.6 agonistic interactions/hour) than stump-tailed macaques. During aggressive encounters, biting is rare and not performed by adult males. In a captive study, coalitions were rarely observed. Females have a mutual embrace in which they meet head to tail and sniff each other's genitals like dogs.

Physical Characteristics:
Head and body length
- Male: 400-500mm (15.7-19.7in)
- Female: 450-550mm (17.7-21.7in)
Weight
- Male: 4.9kg (10.9lb)
- Female: 6kg (13.2lb)
Habitat:
Taiwan
Mixed coniferous-hardwood temperate forest, as well as bamboo and grassland at 100-3600m (328-11,812ft).
Diet
Fruit, leaves, animal prey, buds, young shoots. These macaques reportedly raid crops.
Behaviour:
Diurnal, arboreal, and terrestrtial. Formosan rock macaques rest in forest and forage in grassland. High-ranking matrilines have more reproductive success. Habitat destruction rather than hunting is the greatest risk to the population.

Physical Characteristics:
Head and body length
- Male: 472-601mm (18.6-23.7in)
- Female: Female: 535-607mm (21.1-23.9in)
Weight
- Male: 8.3-18.0kg (18.3-39.7lb)
- Female: 11.0-18.0kg (24.2-39.7lb)
Habitat:
Japan
Subtropical to subalpine, deciduous, broadleaf, and ever green forest of Japan below 1500m (4922ft). This macaque lives at the northernmost latitude of any nonhuman primate. An introduced free-ranging population has lived in Texas (USA) since 1972.
Diet
Fruit, seeds, leaves, bark, fungi, bird eggs, and invertebrates such as snails and cray fish.
Behaviour:
Diurnal, arboreal, and terrestrtial. Japanese macaques are good swimmers. This species often invades human territories, including hot thermal baths in the winter.
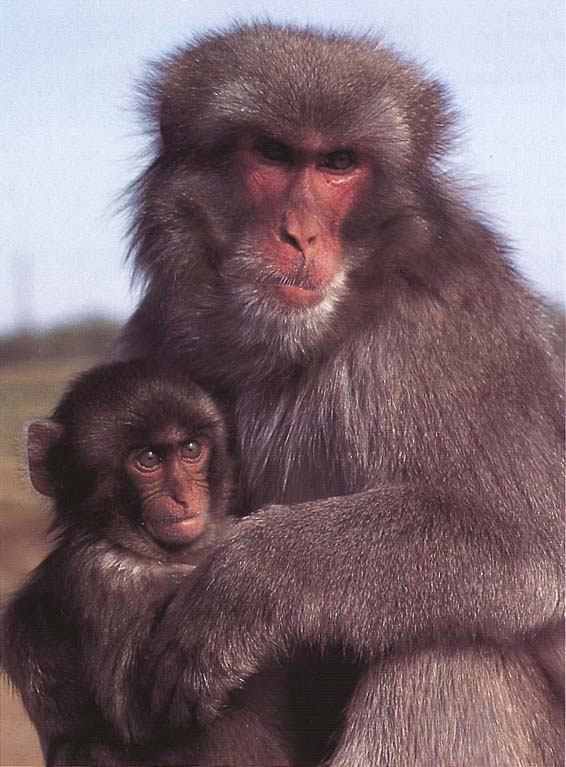

Physical Characteristics:
Head and body length
- Male: 472-601mm (18.6-23.7in)
- Female: Female: 535-607mm (21.1-23.9in)
Weight
- Male: 8.3-18.0kg (18.3-39.7lb)
- Female: 11.0-18.0kg (24.2-39.7lb)
Habitat:
Japan
Subtropical to subalpine, deciduous, broadleaf, and ever green forest of Japan below 1500m (4922ft). This macaque lives at the northernmost latitude of any nonhuman primate. An introduced free-ranging population has lived in Texas (USA) since 1972.
Diet
Fruit, seeds, leaves, bark, fungi, bird eggs, and invertebrates such as snails and cray fish.
Behaviour:
Diurnal, arboreal, and terrestrtial. Japanese macaques are good swimmers. This species often invades human territories, including hot thermal baths in the winter.
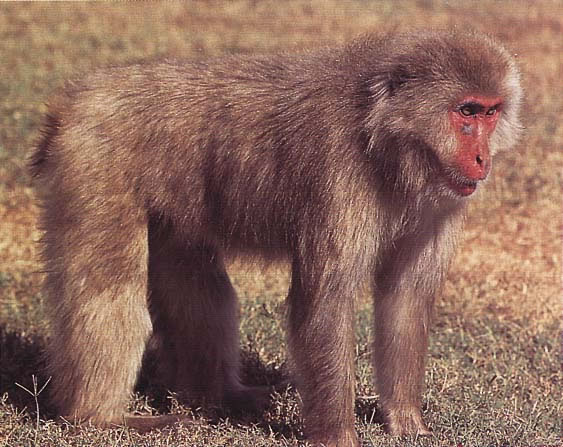

Physical Characteristics:
Head and body length
- Male: 472-601mm (18.6-23.7in)
- Female: Female: 535-607mm (21.1-23.9in)
Weight
- Male: 8.3-18.0kg (18.3-39.7lb)
- Female: 11.0-18.0kg (24.2-39.7lb)
Habitat:
Japan
Subtropical to subalpine, deciduous, broadleaf, and ever green forest of Japan below 1500m (4922ft). This macaque lives at the northernmost latitude of any nonhuman primate. An introduced free-ranging population has lived in Texas (USA) since 1972.
Diet
Fruit, seeds, leaves, bark, fungi, bird eggs, and invertebrates such as snails and cray fish.
Behaviour:
Diurnal, arboreal, and terrestrtial. Japanese macaques are good swimmers. This species often invades human territories, including hot thermal baths in the winter.

|
|
|
|
Resources
Personnel / Staff |
B virus / Macaques |
Our Research |
